

Myopia
What Is Myopia (Nearsightedness)?
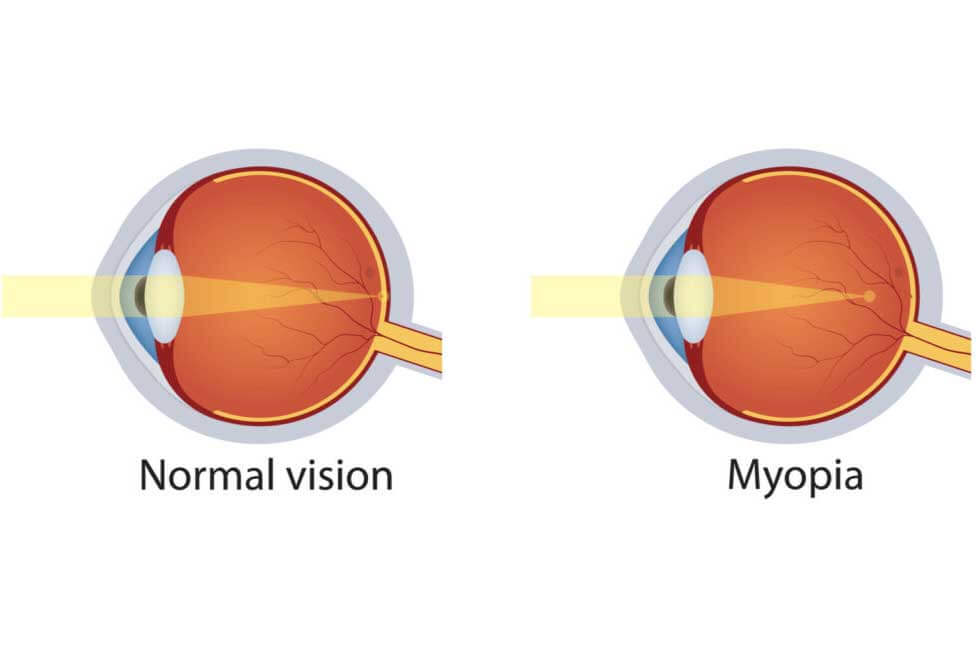
Is it tough to see distant objects like road traffic signs, till you’re some feet away, however, to read a book would be easy. Chances are you’re myopic, which is also referred to as nearsighted. It’s a quite common condition that your eye ophthalmologist usually can fix with eyeglasses, contact lenses or eye surgery.
What Causes Myopia?
The structure of your eye is to blame. When your eyeball is just too lengthy or the cornea, the protective outer layer of your eye is just too curved, the light that enters your eye won’t recognize correctly. The image focuses in front of the retina, the light-sensitive part of your eye, in preference to directly on the retina. These are the reasons for blurred vision. Doctors also call this a refractive error.
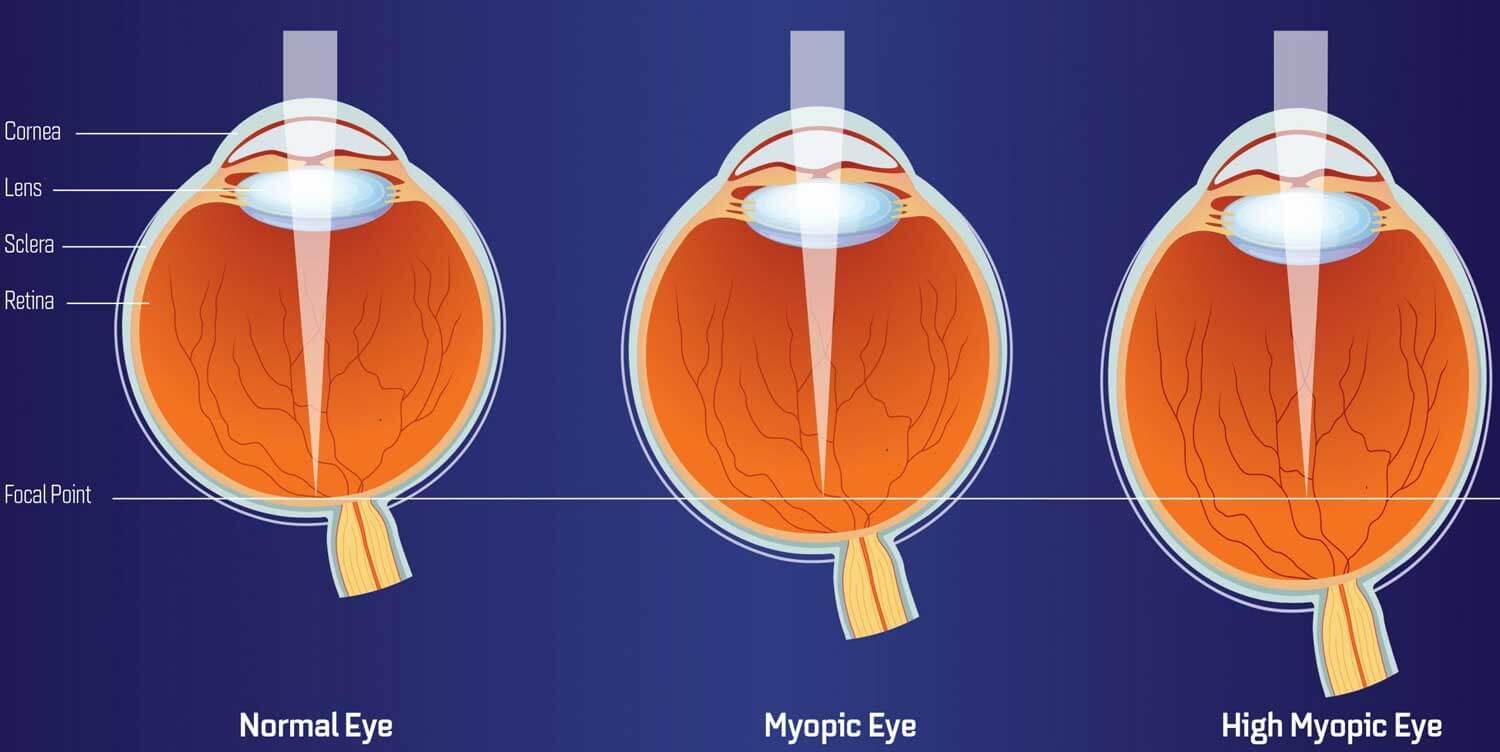
High myopia
It’s an extra serious form of the situation and condition, in which the eyeball grows greater than it is meant to and turns into a very long front to back. Besides making it tough to look at things at a distance, it could also enhance your threat of having other situations and conditions like a detached retina, cataracts and glaucoma.
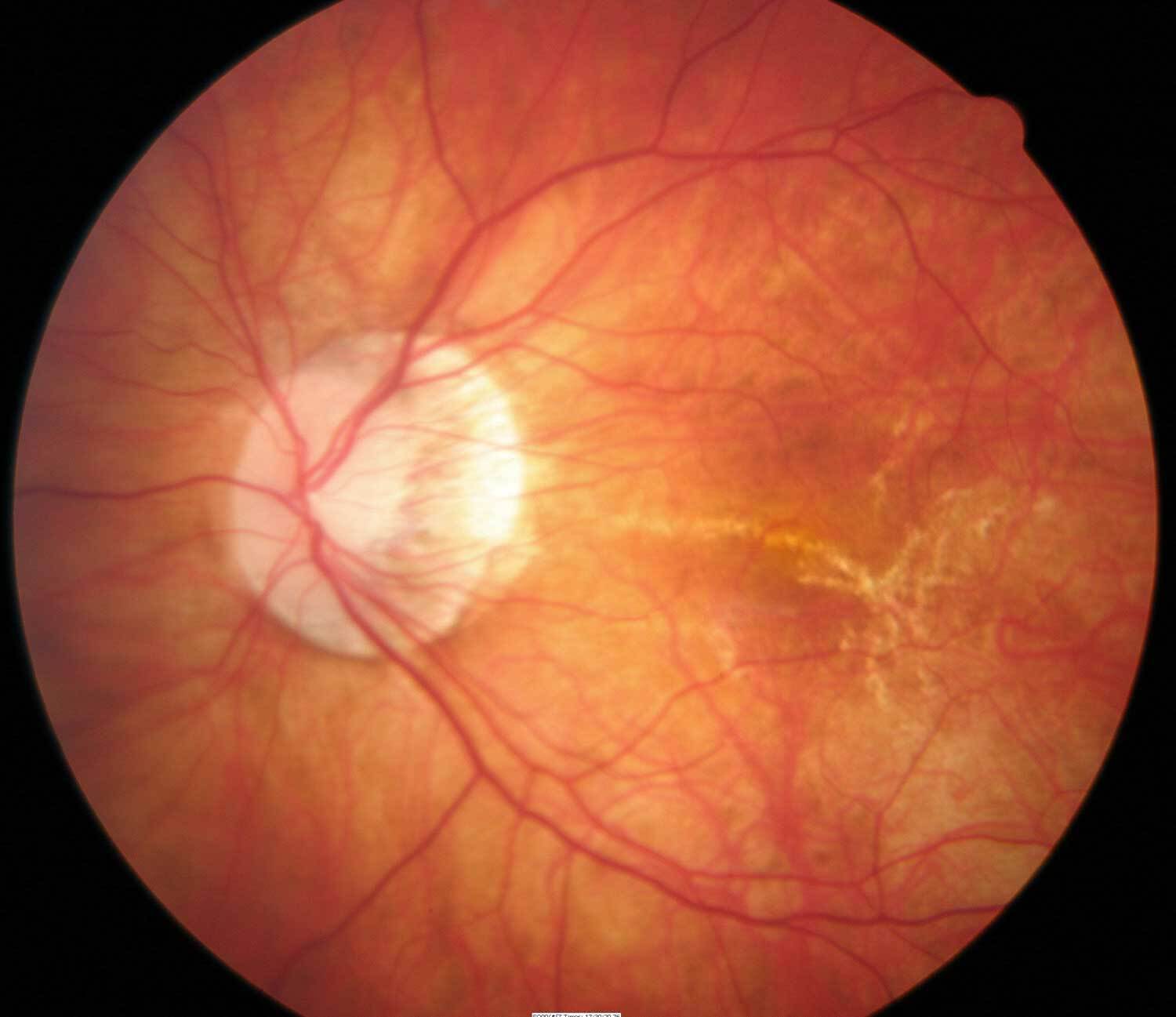
Degenerative Myopia
We also called pathological or malignant myopia; it’s far an extraordinary type you typically inherit from your parents. Very quickly your eyeball gets longer and causes extremely severe myopia, usually by the teenage or early adult years. This form of myopia can get worse far into adulthood. Besides making it hard to see objects at a distance, you could have a higher threat of having a detached retina, abnormal blood vessel growth in the eye called as choroid neovascularization and glaucoma.
Symptoms
The only most superficial symptom is that more significant distant objects are blurred. Also, few symptoms like headaches, squinting, eye stress, and eye fatigue when you see objects from more than a few feet away. Many children with myopia regularly have trouble studying or reading on the blackboard at school.
Diagnosis and Treatment
An eye examination can show you if you’re myopic. Glasses, contact lenses or refractive surgery can usually correct the eye problem. When you’ve got myopia, your prescription for glasses or contact lenses might be a negative number. The more poor the range of negative numbers, the stronger your lenses will be. Your prescription enables the eye to focus light on your retina which clears up your vision.
Eye surgical procedures can improve your vision a lot, as you could not need to wear glasses or contact lenses. The most common procedures for myopia are Photorefractive Keratectomy, Lasik, EVO implantable Collamer lens (ICL) and Orthokeratology.
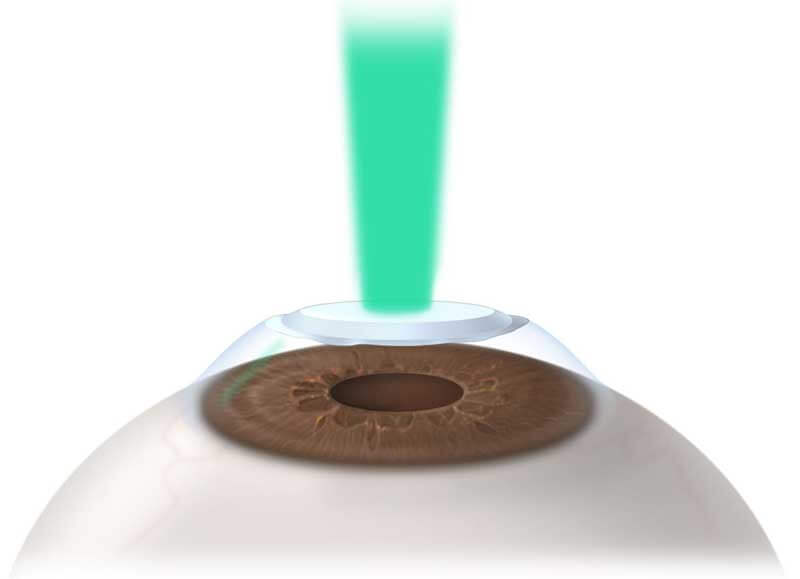
Photorefractive Keratectomy
Also referred to as PRK, this surgery makes use of a laser to sculpt the center layer of your cornea. That flattens the cornea’s curve and lets light rays focus closer to or on your retina.

Lasik
The most common surgical operation for myopia is Lasik. The eye surgeon uses a laser or any other tool to create a thin flap on the top layer of your cornea. They sculpt the cornea with another laser and move the flap returned into place.
EVO Implantable Collamer Lens (ICL)
By using a microscopic incision, a contact lens made of soft polymeric material is implanted into your eye between your natural lens and your iris. It assists refract light on the retina, producing clearer vision.
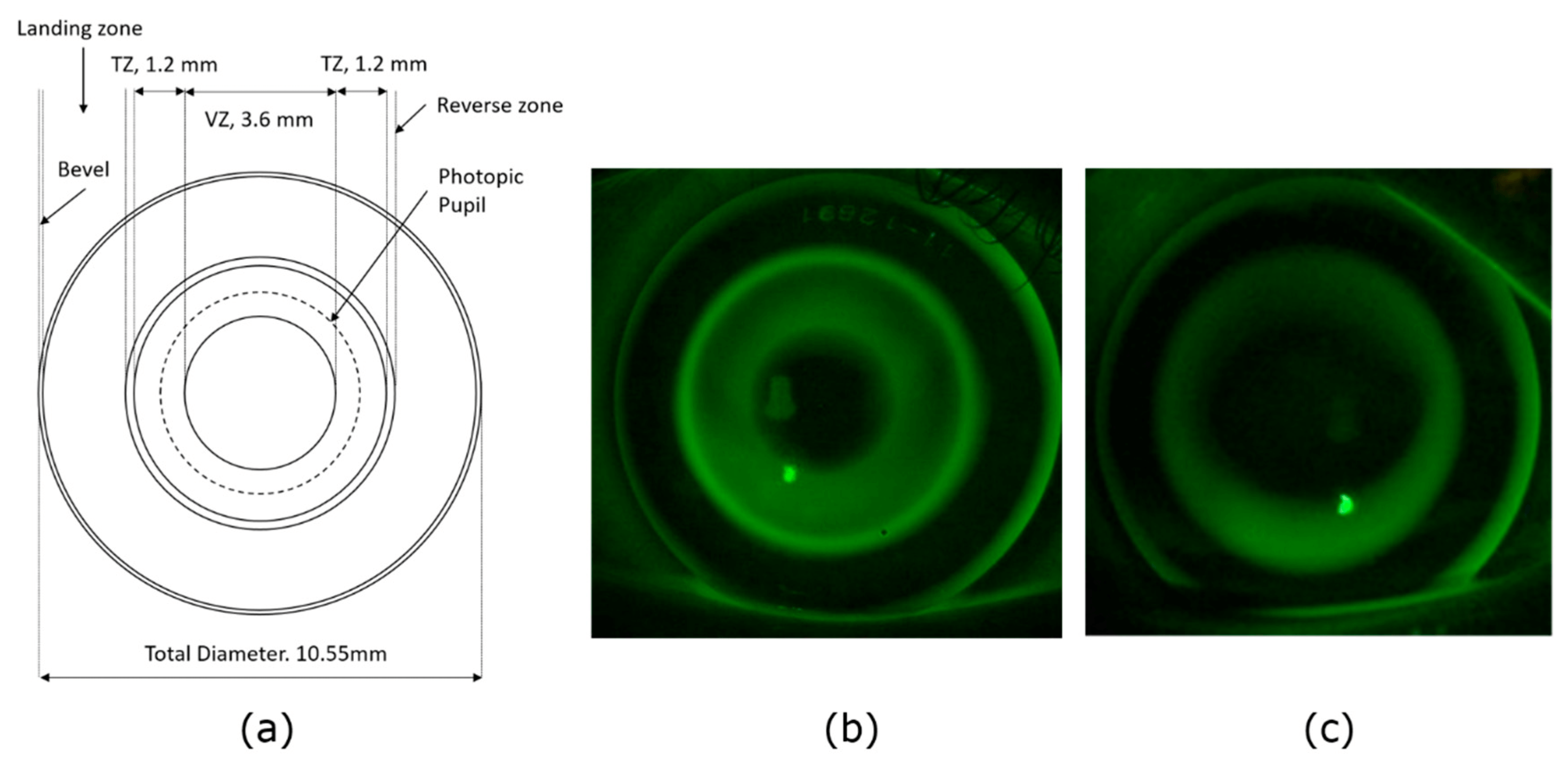
Orthokeratology
Orthokeratology or Ortho-k is the process of deliberately reshaping the anterior cornea by utilizing specialty contact lenses to temporarily and reversibly reduce refractive error after lens removal. Ortho-k is mostly used to correct near-sightedness (myopia) for kids and adults too.
In the case of excessive myopia, special contacts or atropine eye drops have been found to be powerful in slowing the development. In some cases, your doctor might also propose a cataract or clean lens replacement surgical procedure.
Myopia runs in families and will likely start in childhood. Multifocal lens (glasses or contacts lens) and eye drops consisting of atropine, pirenzepine gel or cyclopentolate can assist slow the progression. Your eyes normally stop converting or changing after your teenage years, but not always. The incidents of myopia have been growing and rising at an alarming rate in latest years. If you notice changes in your vision, immediately get your eyes checked by an ophthalmologist or by a retina specialist.

