

OCULAR INJURY
Best Advanced Treatment for Ocular Injuries and Common Eye Injuries
An ocular injury refers to any trauma or damage to the eye or its surrounding structures. These injuries can range from minor irritations to severe trauma that threatens vision loss or even permanent blindness. Immediate assessment and treatment are essential to prevent complications and preserve eye health.
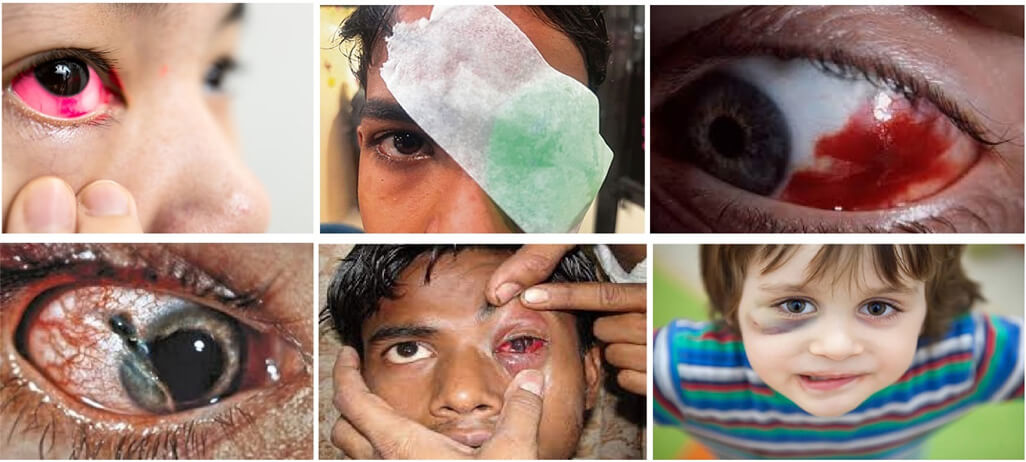
Types of Ocular Injuries
Ocular injuries are classified based on the location and severity of the damage:
Surface Eye Injuries
- Corneal abrasion (scratched eye)
- Foreign body in the eye (dust, metal, debris)
- Chemical burns
Blunt Trauma
- Black eye (periorbital hematoma)
- Hyphema (bleeding in the front of the eye)
- Orbital fractures
Penetrating or Perforating Injuries
- Lacerations or puncture wounds to the globe
- Intraocular foreign body
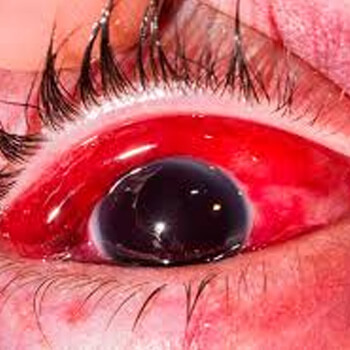
Internal Eye Injuries
- Retinal detachment
- Vitreous hemorrhage
- Lens dislocation
- Optic nerve trauma
Common Causes of Ocular Injuries
- Sports injuries (e.g., basketball, baseball, racquetball)
- Workplace accidents involving chemicals or tools
- Motor vehicle collisions
- Falls or blunt impact
- Chemical exposure
- Foreign body entry into the eye (metal, wood, glass)
- Violence or assault
Symptoms of Ocular Injury
Depending on the type of injury, symptoms may include:
- Eye pain or pressure
- Redness and tearing
- Blurred or double vision
- Light sensitivity (photophobia)
- Swelling around the eye
- Floaters or flashes of light
- Blood in the eye (subconjunctival hemorrhage or hyphema)
- Visible deformity or laceration
First Aid for Eye Injuries
Basic first aid steps depend on the type of ocular trauma:
- Do not rub the eye under any circumstances
- Flush the eye with clean water in case of chemical exposure
- Cover the eye with a sterile shield for protection (not pressure)
- Do not attempt to remove embedded foreign objects
- Seek emergency eye care immediately
Medical Treatment for Ocular Injuries
Treatment will depend on the nature and severity of the injury. Medical care may involve:
- Topical antibiotics or steroid drops
- Suturing of lacerations
- Surgical repair (e.g., for ruptured globe or retinal detachment)
- Removal of foreign body
- Tetanus shot if required
- Imaging (CT scan, ultrasound) for internal injuries
When to Seek Emergency Eye Care
Call a doctor or go to the emergency room immediately if:
- You experience sudden or severe vision loss
- There’s persistent bleeding or discharge from the eye
- The eye is protruding or sunken
- You suffer a blow to the head with vision changes
- There’s a sharp object penetrating the eye
Preventing Ocular Injuries
- Always wear protective eyewear during sports, construction, or lab work
- Follow safety protocols in the workplace
- Keep hazardous chemicals properly labeled and stored
- Use caution when handling sharp tools or machinery
- Supervise children around sharp or dangerous objects
Ocular injuries can range from mild discomfort to life-altering trauma. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can make the difference between full recovery and permanent damage. If you suffer any kind of eye trauma, don’t wait—seek medical attention immediately to protect your vision and eye health.
Common Eye Injuries and Their Treatment Options
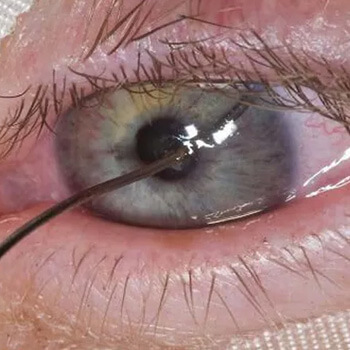
Penetrating Eye Injury: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Prevention
A penetrating eye injury is a serious type of ocular trauma where a foreign object pierces the eyeball, often leading to vision loss or permanent damage. This type of eye injury requires emergency medical attention to preserve vision and prevent complications like infection or retinal detachment.
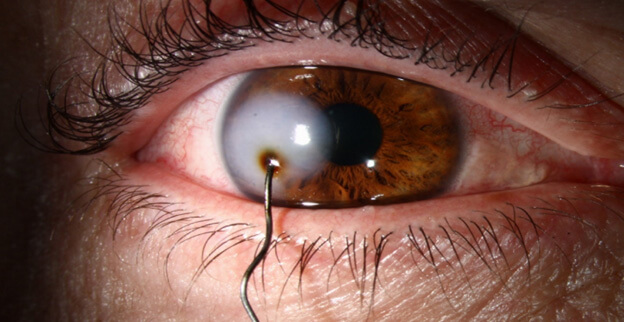
What Is a Penetrating Eye Injury?
A penetrating eye injury occurs when an object enters the eye but does not exit. Unlike perforating injuries, which involve both an entry and exit wound, penetrating injuries involve only one wound and can cause significant internal damage to eye structures such as the cornea, sclera, lens, or retina.
Common Causes
- High-speed metal fragments (e.g., from hammering or grinding)
- Glass shards from accidents
- Wood splinters or nails
- Fireworks or explosive trauma
- Industrial or workplace accidents
Symptoms of a Penetrating Eye Injury
- Sudden, severe eye pain
- Blurred or lost vision
- Visible object protruding from the eye
- Bleeding from the eye
- Sensitivity to light
- Eye discharge or tearing
Emergency Treatment
Immediate care is critical. Do not attempt to remove any object from the eye. Cover the eye with a rigid shield (not pressure) and seek emergency ophthalmic care.
Hospital treatment may involve:
- Imaging tests (CT scan of the orbit)
- Surgical removal of foreign body
- Antibiotics to prevent endophthalmitis
- Possible reconstructive surgery
Long-Term Complications
- Infection (e.g., endophthalmitis)
- Retinal detachment
- Cataract formation
- Vision loss or blindness
Prevention Tips
- Always wear protective eyewear during high-risk activities
- Use face shields in industrial settings
- Educate workers on eye safety protocols
- Keep sharp objects away from children’s reach
Final Thoughts
A penetrating eye injury is a medical emergency that can have lifelong consequences if not treated promptly. Awareness, prevention, and rapid intervention are key to preserving vision. If you or someone around you suffers from a serious eye injury, seek immediate emergency care from an ophthalmologist.
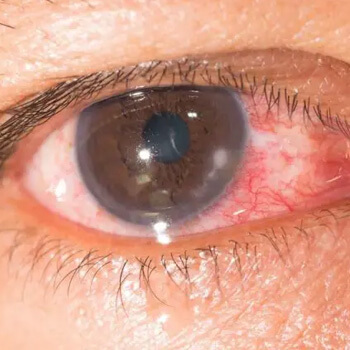
Corneal Abrasions (Scratched Eye): Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
A corneal abrasion, commonly known as a scratched eye, is one of the most frequent types of eye injuries. It occurs when the cornea—the clear, protective outer layer of the eye—is scratched by a foreign object or surface. While typically minor, corneal abrasions can be extremely painful and require proper care to prevent complications like infection or vision problems.
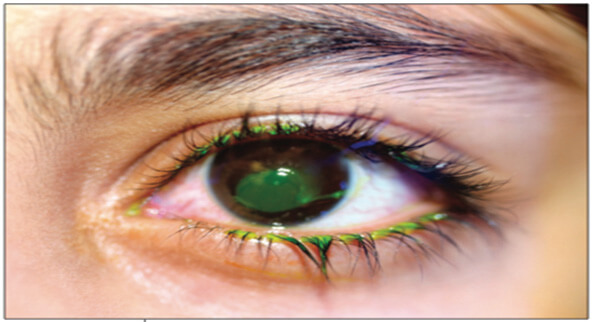
What Causes a Corneal Abrasion?
Corneal abrasions can be caused by a variety of everyday occurrences, including:
- Foreign objects such as dust, sand, or eyelashes
- Contact lens overuse or mishandling
- Rubbing your eyes vigorously
- Tree branches, paper edges, or fingernails
- Workplace accidents or sports injuries
Common Symptoms of a Scratched Cornea
Symptoms of a corneal abrasion can appear immediately and may include:
- Sharp eye pain
- Feeling like something is in your eye (foreign body sensation)
- Redness and tearing
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Blurred vision
- Eye twitching or excessive blinking
How Is a Corneal Abrasion Diagnosed?
An eye doctor (optometrist or ophthalmologist) will use a fluorescein dye test and a slit lamp exam to view the extent of the abrasion. Immediate evaluation is crucial to rule out deeper injuries or corneal ulcers.
Treatment Options for Corneal Abrasions
Most minor corneal abrasions heal within 24–72 hours. Treatment may include:
- Lubricating eye drops or artificial tears
- Antibiotic eye drops to prevent infection
- Pain relief medications
- Avoiding contact lenses until healed
- Wearing sunglasses to reduce light sensitivity
DO NOT rub the eye, and avoid using over-the-counter redness-reducing drops unless advised by a doctor.
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe or persistent eye pain
- Blurry or worsening vision
- Signs of infection (pus, swelling, increasing redness)
- Pain when opening or closing the eye
Preventing Corneal Abrasions
- Always wear protective eyewear during work, sports, or yard work
- Use care when removing or inserting contact lenses
- Avoid rubbing your eyes, especially with dirty hands
- Regularly clean lenses and eye gear
Final Thoughts
While a corneal abrasion may seem like a minor eye injury, it can be very painful and should not be ignored. With prompt treatment and proper care, most scratched eyes heal quickly without long-term damage. Protect your vision by recognizing symptoms early and seeing an eye care professional if needed.
Ashu Laser Vision specializes in advanced corneal abrasion treatment in Andheri, Mumbai, ensuring quick and effective recovery.
Impact Injuries from Sports and Accidents: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Impact injuries are a common result of sports activities and accidental trauma. These injuries occur when a sudden force or collision damages soft tissue, bones, or joints. Whether it’s a sports injury from a fall, tackle, or collision, or an accident-related injury like a slip or car crash, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for full recovery.
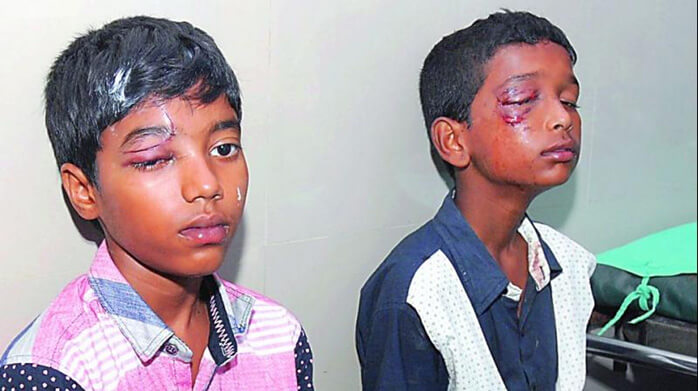
What Are Impact Injuries?
An impact injury occurs when the body is struck with force, often causing bruising, swelling, fractures, or soft tissue damage. These injuries can range from minor to severe and commonly affect:
- Muscles and ligaments
- Bones and joints
- Head and spine
- Eyes and face
Common Causes of Impact Injuries
1. Sports Injuries
- Football tackles
- Basketball collisions
- Soccer falls and kicks
- Contact sports like hockey or rugby
2. Accidental Trauma
- Car or motorcycle accidents
- Falls from height
- Workplace injuries
- Slips and trips at home
Signs and Symptoms of Impact Injuries
Symptoms vary depending on the body part involved and the severity of the injury:
- Sudden, sharp pain
- Swelling and bruising
- Limited mobility or joint stiffness
- Tenderness to the touch
- In severe cases: fractures, dislocations, or concussions
Treatment Options for Impact Injuries
Immediate Care (R.I.C.E. Method):
- Rest the injured area
- Ice to reduce swelling
- Compression with a bandage
- Elevation to reduce inflammation
Medical Treatment May Include:
- Pain medications or anti-inflammatories
- Physical therapy
- X-rays or MRIs to rule out fractures
- Surgical intervention for severe cases
Preventing Sports and Impact Injuries
- Always wear protective gear (helmets, pads, mouthguards)
- Warm up and stretch before physical activity
- Use proper form and technique
- Avoid playing while fatigued or injured
- Follow safety protocols in workplaces and recreational settings
When to Seek Medical Attention
Seek immediate care if you experience:
- Persistent or severe pain
- Visible deformity or bone protrusion
- Loss of movement or sensation
- Dizziness or confusion after a head injury
- Sudden swelling or bruising
Final Thoughts
Impact injuries from sports and accidents can affect anyone—athletes, workers, or everyday individuals. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is key to preventing long-term damage. Whether it’s a sports-related injury or a blunt trauma from an accident, early evaluation by a healthcare provider ensures proper healing and reduces the risk of complications.
At Ashu Eye Hospital, our specialists provide immediate and effective treatment in Mumbai for impact-related eye trauma.
Chemical Burns and Exposure: Symptoms, First Aid, and Prevention
Chemical burns are serious injuries caused by exposure to corrosive substances such as acids, alkalis, or industrial chemicals. These injuries can occur at home, in the workplace, or during industrial accidents, and they require immediate medical attention to prevent lasting damage.
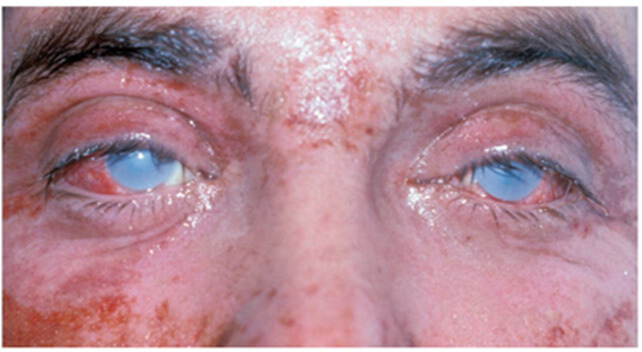
What Are Chemical Burns?
A chemical burn (also known as a caustic burn) occurs when a harmful chemical comes into contact with the skin, eyes, mouth, or internal organs. These burns can range from mild irritation to deep tissue destruction and may not always cause immediate pain, making them deceptively dangerous.
Common Causes of Chemical Burns and Exposure
Chemical burns can result from contact with:
- Household cleaners (bleach, ammonia, drain cleaners)
- Industrial chemicals (acids, alkalis, solvents)
- Battery acid
- Laboratory substances
- Agricultural chemicals (fertilizers, pesticides)
Exposure routes include:
- Skin contact
- Inhalation
- Eye exposure
- Ingestion
Symptoms of Chemical Burns
Symptoms vary based on the type of chemical and area affected but may include:
- Redness, irritation, or blistering of the skin
- Pain or burning sensation
- Swelling or numbness
- Vision loss or eye pain (for eye exposure)
- Difficulty breathing or coughing (for inhalation exposure)
First Aid for Chemical Burns
Immediate first aid is essential to minimize damage:
- Remove contaminated clothing
- Rinse the affected area with cool, running water for at least 15–30 minutes.
- Do not apply ointments or neutralizing agents.
- Flush eyes thoroughly if exposed—keep eyelids open.
- Seek emergency medical care
If the chemical is powdered (like lime), brush it off dry before rinsing.
Medical Treatment for Chemical Burns
Medical care for chemical exposure may involve:
- Wound cleaning and decontamination
- IV fluids for hydration and flushing
- Pain management
- Antibiotics to prevent infection
- Surgical treatment for severe burns (e.g., skin grafts)
- Specialist care for eye injuries or inhalation
Preventing Chemical Exposure and Burns
- Wear protective gear (gloves, goggles, masks) when handling chemicals
- Read and follow safety labels and instructions
- Store chemicals securely and out of reach of children
- Use proper ventilation when working with hazardous substances
- Get trained on workplace chemical safety protocols
When to Seek Emergency Medical Help
Call emergency services if:
- The burn covers a large area
- The chemical burn involves the eyes, face, groin, or hands
- There is difficulty breathing
- The victim experiences shock, confusion, or unconsciousness
- Pain worsens despite initial care
Final Thoughts
Chemical burns and exposure can be life-threatening without fast and proper treatment. Whether at home or on the job, knowing how to recognize symptoms, administer first aid, and take preventive safety measures is key to reducing risk and protecting long-term health.
At Ashu Laser Vision, we provide comprehensive care for chemical eye injuries in Mumbai to minimize the risk of permanent damage.
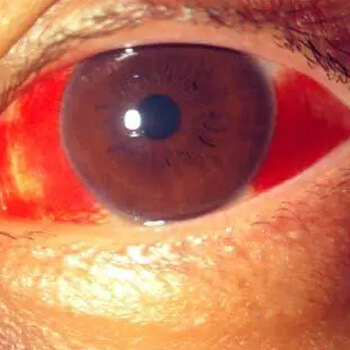
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage (Eye Bruise): Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
A subconjunctival hemorrhage, often referred to as an eye bruise, occurs when a small blood vessel breaks just underneath the clear surface of your eye (conjunctiva). Though it may look alarming—a bright red patch on the white of the eye—it’s usually harmless and resolves on its own without treatment.
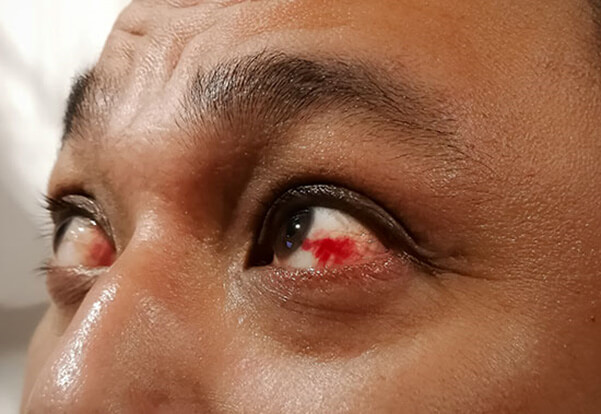
What Is a Subconjunctival Hemorrhage?
A subconjunctival hemorrhage is a condition where blood leaks into the space between the conjunctiva and the sclera (white part of the eye). Because the conjunctiva can’t absorb blood quickly, the red spot often stays visible for days or even weeks.
Common Causes of Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
While usually not a serious condition, a subconjunctival hemorrhage can be caused by:
- Sneezing, coughing, or vomiting (sudden pressure increase)
- Heavy lifting or straining
- Eye rubbing or trauma
- High blood pressure
- Blood-thinning medications (e.g., aspirin, warfarin)
- Minor eye injury or contact lens irritation
Symptoms of a Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
This condition is usually painless and does not affect vision, but typical symptoms include:
- Bright red or dark patch on the white of the eye
- No discharge or tearing
- No changes in vision
- Mild eye irritation or a “scratchy” feeling
Is It Dangerous? When to Worry
While most cases are benign, you should see an eye doctor if:
- The redness persists longer than 2–3 weeks
- You experience pain, vision changes, or recurring hemorrhages
- There’s blood in both eyes or the eye is swollen
- You’re on blood thinners or have a bleeding disorder
Treatment for Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
Most eye bruises heal on their own within 7–14 days without any specific treatment. However, to support healing:
- Artificial tears can reduce irritation
- Avoid rubbing your eyes
- Monitor blood pressure if applicable
- Review medications with your doctor if on anticoagulants
How to Prevent a Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
- Manage underlying conditions like hypertension
- Use protective eyewear during high-risk activities
- Avoid straining during bowel movements or heavy lifting
- Practice gentle eye care and proper contact lens hygiene
Final Thoughts
A subconjunctival hemorrhage may look frightening, but it’s typically harmless and self-resolving. Understanding the causes and symptoms can help ease concerns and ensure you take the right steps toward eye health. If in doubt, always consult with an eye care professional to rule out any underlying issues.
At Ashu Eye Hospital, we offer expert monitoring and management for subconjunctival hemorrhage cases.
Deep Scratches or Lacerations: Causes, Treatment, and When to Seek Help
Deep scratches and lacerations are common injuries that involve a break in the skin caused by sharp objects or trauma. Unlike superficial wounds, deep lacerations can damage underlying tissues such as muscles, tendons, or blood vessels and often require medical attention to prevent infection, minimize scarring, and promote proper healing.
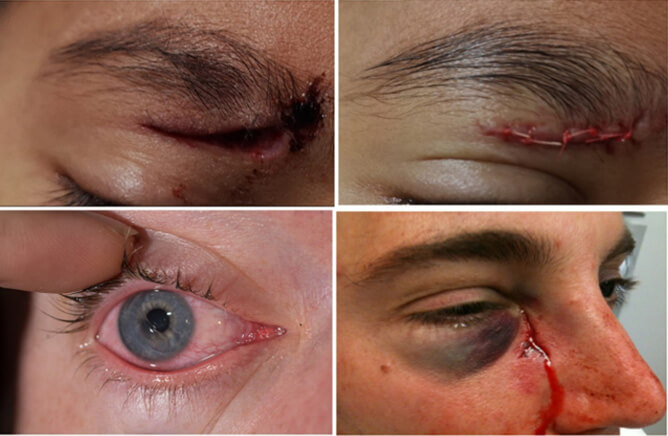
What Are Deep Scratches and Lacerations?
A laceration is a deep cut or tear in the skin, often caused by sharp instruments, machinery, or accidents. A deep scratch may appear thinner but can still penetrate into the dermis or subcutaneous layer, especially when caused by animal claws, thorns, or broken glass.
Common Causes of Deep Cuts and Scratches
- Workplace accidents involving tools or machinery
- Falls onto sharp objects or debris
- Animal bites or scratches
- Broken glass or metal edges
- Sports injuries (especially in contact sports)
- Kitchen accidents (e.g., knife slips)
Symptoms of Deep Lacerations
Symptoms may include:
- Profuse or continuous bleeding
- Pain, especially with movement
- Swelling, bruising, or redness
- Exposed fat, muscle, or tendon
- Numbness or tingling (possible nerve damage)
First Aid for Deep Scratches and Lacerations
Proper first aid is critical to minimize risk of infection and speed up healing:
- Stop the bleeding – Apply direct pressure with a clean cloth or sterile bandage.
- Clean the wound gently with sterile saline or water.
- Do not remove deeply embedded objects—seek professional help.
- Apply a clean bandage and elevate the injured area.
- Seek medical attention for deep or gaping wounds.
Medical Treatment for Deep Lacerations
A healthcare provider may offer:
- Stitches (sutures) or staples to close the wound
- Tetanus shot if the injury is from a dirty or rusty object
- Antibiotics to prevent infection
- Wound debridement if there is tissue damage or contamination
- Scar management therapy or follow-up care
When to Seek Emergency Care
Go to the ER or urgent care if:
- The wound is longer than half an inch or gaping open
- You cannot control the bleeding after 10–15 minutes
- You see bone, tendon, or fat
- The wound is caused by a bite, rusted metal, or dirty object
- You experience numbness, weakness, or signs of infection
Preventing Deep Scratches and Lacerations
- Wear protective gloves and clothing when handling sharp tools
- Use proper technique when cutting or working with machinery
- Keep sharp objects stored safely away from children
- Wear safety gear during sports or outdoor work
- Keep pets groomed and supervised around young children
Final Thoughts
Deep scratches and lacerations should never be ignored, especially when bleeding is persistent or the wound appears deep. Immediate first aid, followed by proper medical treatment, ensures faster healing and lowers the risk of infection or complications. If in doubt, it’s always safer to get a wound evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Ashu Laser Vision and Ashu Eye Hospital offer expert surgical intervention for deep ocular injuries.
Retinal and Ocular Trauma: Types, Symptoms, and Emergency Treatment
Retinal and ocular trauma refers to serious injuries affecting the retina or other internal structures of the eye. These injuries often result from blunt force, penetrating trauma, or accidents, and can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated promptly. Immediate evaluation by an eye care specialist is essential to prevent complications and preserve sight.
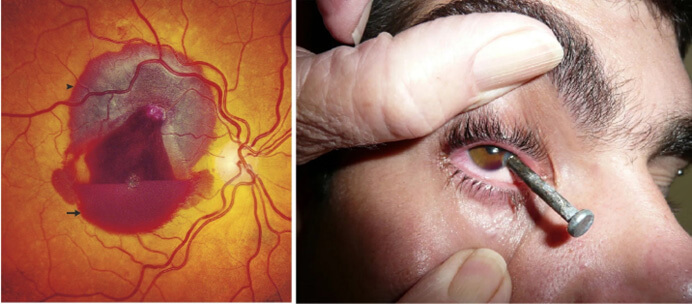
What Is Ocular Trauma?
Ocular trauma includes any injury to the eye or surrounding orbital structures, from mild surface scratches to severe internal damage. It’s a leading cause of monocular blindness (blindness in one eye) worldwide and can involve structures like the cornea, lens, retina, or optic nerve.
Understanding Retinal Trauma
Retinal trauma is a form of internal eye injury affecting the retina, the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. Damage to the retina can cause sudden or progressive vision loss, depending on the severity.
Common Retinal Injuries:
- Retinal detachment
- Commotio retinae (bruising of the retina)
- Retinal hemorrhage
- Macular hole
- Choroidal rupture
Causes of Retinal and Ocular Trauma
- Blunt force trauma (sports injuries, fists, airbags)
- Penetrating eye injuries (metal fragments, glass, sharp objects)
- Falls or motor vehicle accidents
- High-impact sports (boxing, hockey, racquetball)
- Explosions or chemical exposure
Symptoms of Retinal and Ocular Injury
Depending on the area affected, symptoms may include:
- Sudden vision loss or blurry vision
- Flashes of light or floaters
- Eye pain or pressure
- Bleeding in or around the eye
- Visible deformity or swelling
- Dark curtain over part of vision (possible retinal detachment)
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
Emergency Treatment for Retinal and Ocular Trauma
Prompt evaluation by an ophthalmologist or eye trauma specialist is critical. Depending on the injury, treatment may include:
- Retinal surgery (e.g., scleral buckle, vitrectomy)
- Laser photocoagulation for retinal tears
- Steroid or anti-inflammatory drops
- Antibiotics for penetrating injuries
- Protective eye shielding
- Hospitalization for severe orbital trauma
Diagnosis: How Eye Trauma Is Evaluated
Doctors may use the following tests to assess trauma:
- Dilated eye exam
- OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
- B-scan ultrasound
- CT scan of the orbits
- Fundus photography
Long-Term Complications of Retinal and Ocular Trauma
Untreated or severe trauma can result in:
- Permanent vision loss
- Retinal scarring
- Macular degeneration
- Secondary glaucoma
- Sympathetic ophthalmia (rare autoimmune response)
Preventing Ocular and Retinal Injuries
- Always wear protective eyewear during high-risk activities or contact sports
- Use safety goggles in industrial or lab settings
- Avoid using fireworks or explosives without supervision
- Educate athletes and workers on eye safety protocols
- Keep sharp objects away from children
Final Thoughts
Retinal and ocular trauma can have devastating effects on your eye health and vision. Early detection and treatment are critical for preserving eyesight. If you experience sudden changes in vision or suffer an injury to the eye, don’t delay—seek emergency eye care immediately.
Our clinic provides cutting-edge treatments for retinal injuries in Andheri Mumbai India, to prevent vision loss and improve recovery outcomes.
FAQs about Ocular Injury
An ocular injury refers to any damage or trauma to the eye, including the eyelid, cornea, lens, retina, or other parts of the eye. It can be caused by physical impact, chemical exposure, or sharp objects, and may result in pain, vision disturbances, or permanent blindness if untreated.
Common causes of ocular injuries include:
- Sports-related impacts (e.g., soccer, basketball)
- Accidents involving sharp objects like sticks, glass, or metal
- Chemical splashes (e.g., cleaning agents)
- Workplace accidents
- Car accidents
You can reduce the risk of ocular injuries by:
- Wearing protective eyewear during sports or work-related tasks.
- Using goggles when handling chemicals.
- Avoiding direct contact with sharp objects near the eye.
- Practicing safe driving to prevent accidents.
Symptoms include:
- Pain or discomfort in the eye
- Redness or swelling
- Tearing or excessive watering
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Blood in the eye
- Floaters or dark spots
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Yes, an ocular injury can potentially cause blindness if it affects vital parts of the eye, such as the retina, cornea, or optic nerve. Timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent vision loss.
A corneal abrasion is a scratch or injury to the cornea, the transparent outer layer of the eye. It is one of the most common ocular injuries and can cause pain, redness, and sensitivity to light. Treatment typically includes antibiotic drops to prevent infection.
An ocular injury is diagnosed through a thorough eye examination, which may include:
- Fluorescein staining to highlight corneal abrasions
- Slit-lamp examination to check for damage to the cornea, lens, or retina
- OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography) for detailed retina imaging
- Ultrasound for detecting foreign objects or retinal damage
Treatment for a blunt force ocular injury depends on the severity and type of damage. Options may include:
- Cold compresses to reduce swelling
- Medications for pain relief
- Surgical intervention, such as a vitrectomy for retinal detachment
- Monitoring intraocular pressure to prevent glaucoma
A hyphema is the accumulation of blood in the anterior chamber of the eye, typically caused by trauma. It can result in pain, blurry vision, and increased intraocular pressure. Immediate medical attention is required to prevent complications like glaucoma or vision loss.
Yes, chemical burns can cause permanent damage to the cornea, retina, and other parts of the eye. It’s important to flush the eyes with water immediately after exposure and seek urgent care to minimize the risk of permanent vision impairment.
Deep ocular lacerations require immediate medical attention, and treatment usually involves:
- Sterile cleaning of the wound
- Surgical repair to close the laceration
- Antibiotic eye drops to prevent infection
- Follow-up care to monitor healing and avoid complications
Retinal detachment is when the retina pulls away from its supporting tissue, often due to trauma or an injury to the eye. It can cause sudden vision loss, flashes of light, or floaters. Vitrectomy surgery may be necessary to repair the retina and restore vision.
Recovery time for an ocular injury depends on the severity of the injury. Minor injuries like corneal abrasions may take a few days to heal, while more severe injuries like retinal detachment or lacerations may require weeks or even months for full recovery.
Laser therapy is often used to treat retinal tears or detachment caused by ocular injuries. It uses focused light to create small burns around the tear, which helps seal the retina to prevent further detachment and preserve vision.
Yes, ocular injuries can cause permanent vision loss if not treated promptly and effectively. Injuries to the cornea, retina, or optic nerve may result in irreversible damage if left untreated. Immediate medical care is crucial to minimize the risk.
If a foreign object (like glass, metal, or dust) enters the eye, it should be removed by a professional. The procedure may involve:
- Flushing the eye with saline
- Using a sterile instrument to remove the object
- In some cases, surgical intervention may be required if the object is deeply embedded
An ophthalmologist is a specialist in diagnosing and treating ocular injuries. They perform detailed eye exams, provide emergency care, recommend treatments (e.g., laser therapy, surgery), and monitor recovery to prevent complications.
If ocular injuries are left untreated, they can lead to:
- Infection (e.g., corneal ulcers)
- Permanent vision loss (due to retinal detachment or optic nerve damage)
- Glaucoma (due to increased intraocular pressure)
- Scarring on the cornea
Yes, sports injuries, especially in high-impact sports like basketball, soccer, or hockey, can lead to ocular trauma. Injuries like blunt force trauma or penetrating injuries can cause significant damage to the eye, including retinal tears and corneal abrasions.
If you experience any of the following after an ocular injury, seek immediate help from an ophthalmologist:
- Severe pain or discomfort
- Blood in the eye
- Sudden vision loss or blurred vision
- Foreign objects in the eye that can’t be removed easily
- Swelling or bruising around the eye
Why Choose Ashu Laser Vision for Ocular Injury Treatment in Andheri, Mumbai?
- Expert Care: Led by Shahnawaz Kazi, an experienced ophthalmologist specializing in ocular trauma and eye injuries.
- State-of-the-Art Technology: We use the latest laser therapy.
- Comprehensive Eye Injury Management: From minor corneal abrasions to major retinal trauma, we offer a full range of services.
- Personalized Care: We focus on quick recovery with minimal discomfort and long-term vision preservation.
With over 15 years of specialized experience in treating ocular injuries, Dr. Shahnawaz Kazi has successfully managed a wide range of eye trauma cases, restoring vision and improving the quality of life for numerous patients. His expertise spans from minor corneal abrasions to more complex cases involving retinal detachment and blunt force trauma. Dr. Kazi’s personalized treatment approach, using the latest technologies and advanced techniques, has made him a trusted name for ocular injury treatment in Mumbai.
Whether it’s a sports-related eye injury, chemical exposure, or a more severe penetrating injury, Dr. Kazi and his team are committed to providing timely and effective care to prevent complications and preserve vision. His comprehensive approach ensures that every patient receives the best possible care, from initial diagnosis to post-treatment recovery.
Trust Dr. Shahnawaz Kazi for expert care in ocular injury management, and experience a faster, safer recovery with the most advanced treatment options available in Andheri, Mumbai.
Book an Appointment Today
If you or someone you know has suffered an eye injury, don’t wait! Early diagnosis and specialized treatment for ocular trauma are crucial for minimizing damage and preserving vision. For Ocular Injury or Ocular Injuries, we are the Best Eye Hospital in Mumbai India, your trusted partner in eye injury treatment.
📞 Call now to schedule your consultation or visit us for urgent eye injury care

