Vision Therapy
Best Vision Therapy for Kids & Adults in Mumbai | Ashu Laser Vision, Andheri

Vision therapy is a specialized, non-invasive form of physical therapy for the eyes and brain designed to enhance visual function beyond what glasses or contact lenses can correct. At Ashu Laser Vision & Ashu Eye Hospital in Andheri, Mumbai, our vision therapy program is tailored to both kids and adults, addressing a wide range of visual issues through engaging, effective methods.
Conditions Treated with Vision Therapy
-

Strabismus (Eye turn or "lazy eye")
A condition where the eyes do not align properly.
-

Amblyopia (Lazy eye)
A condition where one eye does not develop normal vision, even with corrective lenses.
-

Convergence Insufficiency
Difficulty focusing both eyes on a nearby object.
-

Binocular Vision Problems
Issues with the coordination of both eyes working together.
-

Eye Tracking and Focusing Issues
Problems with the eyes’ ability to move smoothly across a page or focus on objects.
-

Visual Perceptual Disorders
Difficulty interpreting visual information, often seen in children with learning disabilities or dyslexia.


How Vision Therapy Works
Customized Exercise Plans
Programs are adapted to each individual's needs and may involve beads, jigsaws, computer tasks, or eye-tracking boards.
State-of-the-Art Technology
We utilize digital training systems, virtual reality devices, and interactive software to make therapy fun and effective.
Progressive Training Protocols
Therapies evolve with progress—starting with simpler tasks and advancing to complex activities that enhance depth perception and ocular coordination.
Ongoing Monitoring & Adjustments
Regular assessments ensure exercises match developmental milestones and visual improvements.
Goals of Vision Therapy
Enhance the focusing ability of the eyes
focusing ability, convergence

Enhance the focusing ability of the eyes
focusing ability, convergence
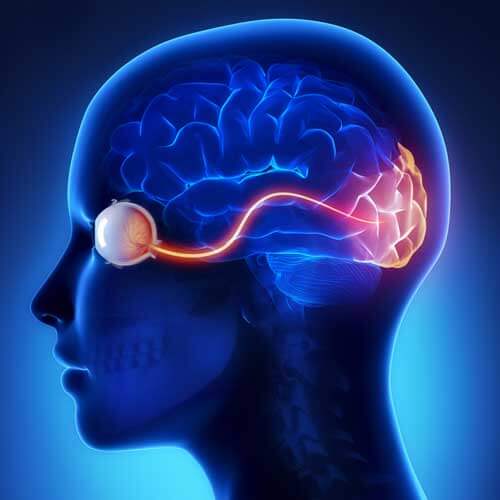
Improve visual processing
how the brain interprets what the eyes see
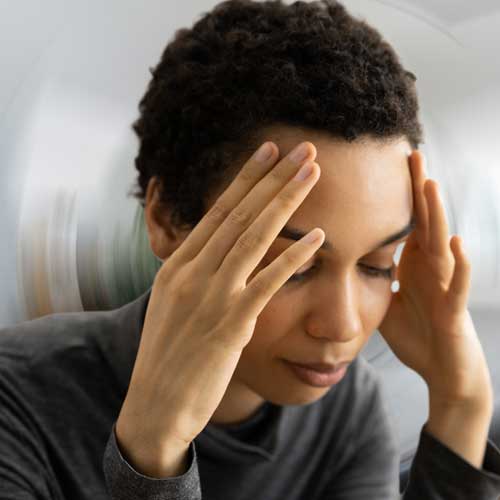

Relieve symptoms like eye strain,
headaches, and double vision
Why Choose Ashu Laser Vision for Vision Therapy
- Experienced Professional Care: Led by pediatric and neuro-vision expert Shahnawaz Kazi, with 16 years of experience.
- Cutting-Edge Vision Therapy Facilities: Equipment’s for digital eye tracking, virtual reality training, and prism systems.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Therapy tailored for different age groups—children, teens, adults—ensuring consistent and measurable progress.
- Holistic Eye Care Integration: Complements treatments like LASIK, oculoplasty, and vision correction with better visual processing.
Vision Therapy Journey: What to Expect
Step | Details |
Initial Assessment | Comprehensive eye exam, binocular vision testing, tracking and focusing analysis |
Custom Plan Design | Exercises and technology-based tasks tailored to diagnose issues |
Weekly Sessions | Typically, 1–2 sessions/week for 8–16 weeks, each session lasting about an hour |
Home Support | Daily 10 – 15-minute exercises to reinforce in-office therapy |
Progress Tracking | Regular evaluations to update exercises and chart improvement |
Completion & Follow-Up | Final evaluation and maintenance exercises to ensure long-term gains |
FAQs – Vision Therapy in Mumbai
- Is vision therapy only for kids?
No—patients of all ages can benefit, including adults with digital fatigue or post-injury visual issues. - How long does therapy take?
Programs typically run for 8–16 weeks, with 1–2 sessions a week. - Are results permanent?
Most patients achieve lasting improvements, especially with compliance and maintenance exercises. - Is therapy fun for children?
We use engaging, interactive tools like VR and computer games to maintain motivation. - Is vision therapy covered by insurance?
Coverage varies; our team at Ashu Laser Vision can provide documentation for reimbursement.
Optimize Vision & Life Skills with Vision Therapy in Mumbai
With a focus on convergence, tracking, and eye-brain interaction, vision therapy plays a crucial role in academic performance, sports, workplace efficiency, and everyday comfort. At Ashu Laser Vision & Ashu Eye Hospital, we offer the best vision therapy services in Mumbai, helping kids and adults reach their full visual potential.
Book your vision therapy consultation at our Andheri center today and experience sharper sight, smarter learning, and sharper focus!
Advanced Vision Therapy for Kids & Adults in Mumbai: A Comprehensive Approach to Eye Health
Vision therapy is not just for children. It is an effective treatment that benefits both kids and adults suffering from visual processing disorders, coordination issues, and other eye problems that go beyond what glasses and contact lenses can fix. At Ashu Laser Vision & Ashu Eye Hospital, located in Andheri, Mumbai, we provide personalized vision therapy solutions to address a wide array of visual challenges and enhance your visual performance.
Key Benefits of Vision Therapy in Mumbai:
- Improved Eye Coordination & Focus: Strengthens the eyes’ ability to work together, improving coordination and reducing eye strain.
- Enhanced Depth Perception: Crucial for sports, driving, and daily activities that require spatial awareness.
- Increased Reading and Learning Efficiency: Helps children and adults with reading difficulties, like dyslexia, ADHD, and learning disabilities.
- Reduced Eye Strain: Particularly helpful for those who spend long hours on digital devices and suffer from digital eye strain or computer vision syndrome.
- Post-Surgery Vision Recovery: Assists in recovery after LASIK or other eye surgeries by improving eye tracking, focusing, and coordination.
Why Vision Therapy is the Best Solution for Children & Adults in Mumbai?
At Ashu Laser Vision & Ashu Eye Hospital, we specialize in treating a wide variety of visual challenges, including strabismus (eye turns), amblyopia (lazy eye), and convergence insufficiency, among others. Here’s why our vision therapy program stands out in Mumbai:
1. Customized Vision Therapy Plans
Every patient is unique. That’s why we design therapy plans that are individualized based on the specific needs of each person. Whether you’re a child with learning-related visual problems or an adult suffering from eye fatigue due to prolonged screen time, we provide a tailored solution.
2. Innovative Technology and Techniques
Our clinic is equipped with the latest technology, including eye-tracking systems, virtual reality, and interactive digital devices. These advanced tools make therapy both effective and engaging for kids and adults alike.
3. Holistic Care and Long-Term Results
We don’t just focus on short-term gains; our vision therapy programs aim for sustainable, long-term improvements. With consistent follow-ups, patients experience lasting changes in their visual abilities, improving quality of life in the long run.
How Vision Therapy Works: Step-by-Step Process
Ashu Laser Vision & Ashu Eye Hospital in Andheri, Mumbai offers a clear roadmap for patients undergoing vision therapy. Here’s how the process works:
1. Initial Evaluation
Your vision therapy journey begins with a thorough eye exam that includes a comprehensive evaluation of your visual skills. This includes testing for eye coordination, focusing ability, and binocular vision problems.
2. Customized Therapy Program
Based on the findings of your evaluation, we design a personalized vision therapy plan that could involve:
- Eye coordination exercises
- Focusing techniques
- Tracking exercises
- Computer-based visual training
- Virtual reality exercises for enhancing depth perception and spatial awareness.
3. Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustments
Throughout your therapy, we monitor your progress and adjust your plan as necessary. This ensures you continue to improve at a steady pace and achieve the best results possible.
4. Post-Therapy Maintenance
After completing your vision therapy, we provide follow-up care and maintenance exercises to reinforce the gains you’ve made. This help maintains the improvements and ensure your visual health remains optimal.
Why Choose Ashu Laser Vision & Ashu Eye Hospital for Vision Therapy in Mumbai?
Here’s why Ashu Laser Vision & Ashu Eye Hospital in Andheri, Mumbai is the leading clinic for vision therapy:
1. Experienced Team of Specialists
Led by Dr. Shahnawaz Kazi, a renowned specialist in pediatric and adult eye care, our team has extensive experience in vision therapy. Dr. Kazi and his team are passionate about offering personalized care to patients of all ages and needs.
2. Comprehensive Services
We offer a one-stop solution for all your vision care needs, including LASIK surgery, pediatric eye care, retinal treatments, and vision therapy. Our holistic approach ensures that you receive the best possible treatment for your eye problems.
3. Advanced Technology and Facilities
At Ashu Laser Vision & Ashu Eye Hospital, we use the latest technology to provide cutting-edge treatments. Our state-of-the-art equipment helps to diagnose and treat a wide variety of eye conditions, providing the best possible outcomes for our patients.
4. Proven Success Rates
Over the years, Ashu Laser Vision & Ashu Eye Hospital has helped thousands of patients in Mumbai achieve clearer, more focused vision. Our success stories speak for themselves, and we are committed to offering the highest standards of care and service.
Common Conditions Treated by Vision Therapy in Mumbai
1. Strabismus (Eye Turn)
- Eye misalignment that results in double vision or a lazy eye.
- Vision therapy helps train the eyes to work together and correct the misalignment.
2. Amblyopia (Lazy Eye)
- A condition where one eye does not develop normal vision, even with glasses or contact lenses.
- Vision therapy can help improve the vision of the weaker eye by stimulating it to focus properly.
3. Convergence Insufficiency
- Difficulty with focusing on near objects, such as when reading or using a phone.
- Therapy involves exercises that strengthen eye muscles to improve focusing ability.
4. Binocular Vision Dysfunction
- Problems with coordinating both eyes together to produce a clear image.
- Vision therapy improves the eyes’ ability to work in sync, reducing headaches and eye strain.
5. Eye Tracking and Focusing Issues
- Difficulty tracking objects or focusing on moving targets.
- A combination of eye exercises and technology-based tasks help improve these skills, especially in children.
6. Visual Perception Problems
- Difficulty interpreting visual information accurately, which can affect learning abilities and daily activities.
- Vision therapy uses exercises that improve the brain’s ability to process and interpret visual cues.
Why Vision Therapy is a Game-Changer for Kids and Adults in Mumbai
Vision therapy goes beyond just improving eyesight—it trains the eyes and brain to work together more effectively, enhancing overall visual skills. Whether you or your child struggle with focusing, eye coordination, or reading difficulties, vision therapy can unlock the full potential of your visual system. By incorporating cutting-edge technology and personalized exercises, our Andheri-based clinic provides effective treatment for a wide range of visual issues, offering lasting improvements that help patients see better and perform better in daily tasks.
Schedule Your Vision Therapy Consultation Today
If you or your child are experiencing eye strain, vision tracking issues, or binocular vision problems, don’t wait to address them. Ashu Laser Vision & Ashu Eye Hospital is the best vision therapy eye hospital in Andheri Mumbai India, we provide the best vision therapy solutions to help you achieve optimal eye health. Whether you’re struggling with amblyopia, strabismus, or convergence issues, our expert team is here to help.
Contact us today to book your consultation and experience the transformative power of vision therapy!
With over 16 years of hands-on experience in Vision Therapy, Dr. Shahnawaz Kazi—renowned eye specialist in Mumbai—has successfully treated countless patients suffering from low vision. His advanced approach to Vision Therapy has delivered outstanding results in low vision treatment, helping patients achieve clearer, more functional vision with long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Vision Therapy
Vision Therapy is a customized program of visual activities and eye exercises prescribed by eye care professionals to improve visual skills such as eye coordination, focusing, tracking, and perception. It’s like physical therapy for the eyes and brain.
Vision Therapy is beneficial for individuals with conditions like lazy eye (amblyopia), strabismus (eye turn), convergence insufficiency, reading difficulties, and visual processing issues, especially in children and students.
Yes, Vision Therapy is highly effective for children, especially those with learning-related vision problems, reading issues, or difficulty concentrating on near tasks.
Absolutely. While children are often ideal candidates, adults with eye strain, concussion-related vision problems, or double vision can also benefit from customized Vision Therapy programs.
A typical Vision Therapy program can range from a few weeks to several months depending on the severity of the condition and the patient’s response. Most programs require weekly sessions and daily home exercises.
Vision Therapy treats conditions such as:
- Amblyopia (lazy eye)
- Strabismus (eye turn)
- Convergence Insufficiency
- Visual processing disorders
- Eye tracking and focusing issues
- Binocular vision dysfunction
Vision Therapy includes eye exercises, but it is much more comprehensive. It involves neurological retraining to improve how the eyes and brain work together, often under professional supervision.
Vision Therapy is not a cure for learning disabilities, but it can correct underlying visual problems that interfere with learning, such as eye tracking and visual memory issues.
Some insurance plans may cover Vision Therapy under orthoptic or neuro-optometric services, but coverage varies. It’s best to check with your provider or ask your Vision Therapy clinic for help with insurance documentation.
Success rates are high, especially for conditions like convergence insufficiency, where studies show over 75% improvement with consistent therapy. Outcomes improve with early diagnosis and patient compliance.
Online or at-home Vision Therapy exercises can support in-clinic treatment, but professional supervision is essential for diagnosis, customization, and effectiveness.
Vision Therapy does not replace glasses, but it can reduce dependency in some cases by improving visual efficiency and helping the eyes work better together.
Common signs include:
- Skipping lines while reading
- Headaches or eye strain
- Short attention span
- Difficulty copying from the board
- Complaints of blurry or double vision
Regular eye exams assess visual acuity and eye health, while a Vision Therapy evaluation tests how the eyes function together, including eye teaming, tracking, and perceptual skills.
Yes, many athletes use Vision Therapy to enhance visual reaction time, hand-eye coordination, and depth perception, all of which are vital in sports.
Vision Therapy is a non-invasive, safe treatment for both children and adults when conducted by qualified eye care professionals.
There’s no “best” age—Vision Therapy can help at any stage of life. However, early intervention in childhood yields the fastest and most effective results.
Vision Therapy is conducted by optometrists specializing in vision development, often with the support of trained Vision Therapy assistants in a clinic setting.
Yes. Vision Therapy can improve focusing flexibility and visual stamina, helping reduce computer vision syndrome symptoms in adults and children.
If you’re searching for Vision Therapy in Mumbai, Dr. Shahnawaz Kazi offers expert, personalized Vision Therapy programs at Ashu Laser Vision Eye Hospital, with over 16 years of proven success in treating both children and adults with visual disorders.

